-
Data Types
JavaScript has several built-in data types that are used to represent different kinds of values. Understanding these data types is important when working with JavaScript code. Primitive Data Types: JavaScript has six primitive data types:
-
Number: Used to represent numeric values, including integers and floating-point numbers.
-
String: Used to represent text values.
-
Boolean: Used to represent true/false values.
-
Undefined: Used to represent a variable that has not been assigned a value.
-
Null: Used to represent a variable that has been explicitly set to a null value.
-
Symbol: Used to represent a unique identifier. Complex Data Types: JavaScript also has two complex data types:
-
Object: Used to represent collections of key/value pairs.
-
Function: Used to represent a block of code that can be executed.
-
String: A sequence of characters, such as"Hello World". Strings can be enclosed in either single or double quotes. -
Number: Numeric values, including integers and floating-point numbers. For example,10and3.14. -
Boolean: Represents a true/false value. The valuestrueandfalseare the only possible values for a Boolean. -
Null: Represents a non-existent value. The valuenullrepresents a deliberate non-value. -
Undefined: Represents a value that has not been assigned. The valueundefinedrepresents a value that has not been assigned or a declared variable that has not been assigned a value. -
Object: A collection of properties and methods. Objects can be created using object literals or with theObjectconstructor. -
Array: An ordered list of values. Arrays are objects and can contain elements of any data type. -
Symbol:A unique and immutable data type that can be used as an identifier for object properties. -
The
typeofoperator in JavaScript is used to determine the data type of a value. It returns a string that represents the data type of the operand. The syntax for usingtypeofis:typeof operand;For example:
let name = 'John Doe'; console.log(typeof name); // "string" let age = 30; console.log(typeof age); // "number" let isMarried = true; console.log(typeof isMarried); // "boolean" let car = null; console.log(typeof car); // "object" let job; console.log(typeof job); // "undefined" -
It's important to note that in JavaScript,
typeof nullreturns "object". This is considered a bug in the language and is a well-known issue. -
The
typeofoperator can be useful for debugging and for checking the data type of a value before performing operations on it. It can also be used to determine if a variable has been declared and assigned a value, by checking if the result oftypeofis "undefined".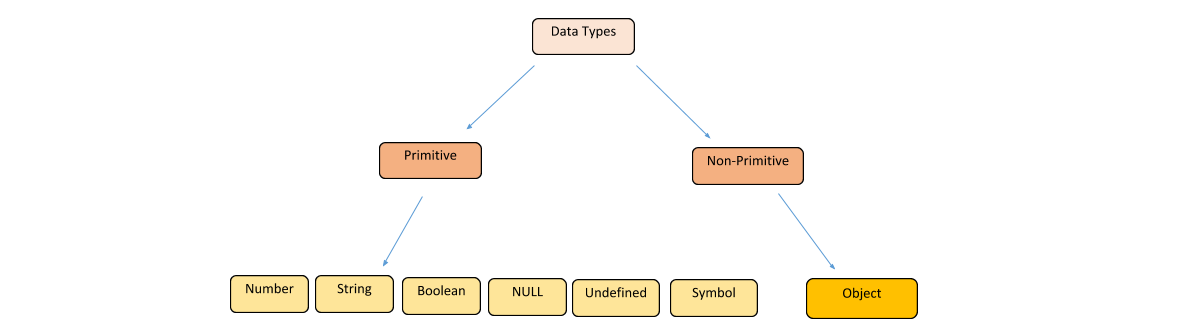
-
Video: "Different Data Types in JavaScript | JavaScript Tutorial | Learn JavaScript" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O9by2KcR2v4 (opens in a new tab)
-
Article: "JavaScript Weekly: Data Types and Mutability" https://medium.com/launch-school/javascript-weekly-data-types-and-mutability-e41ab37f2f95 (opens in a new tab)
-
-